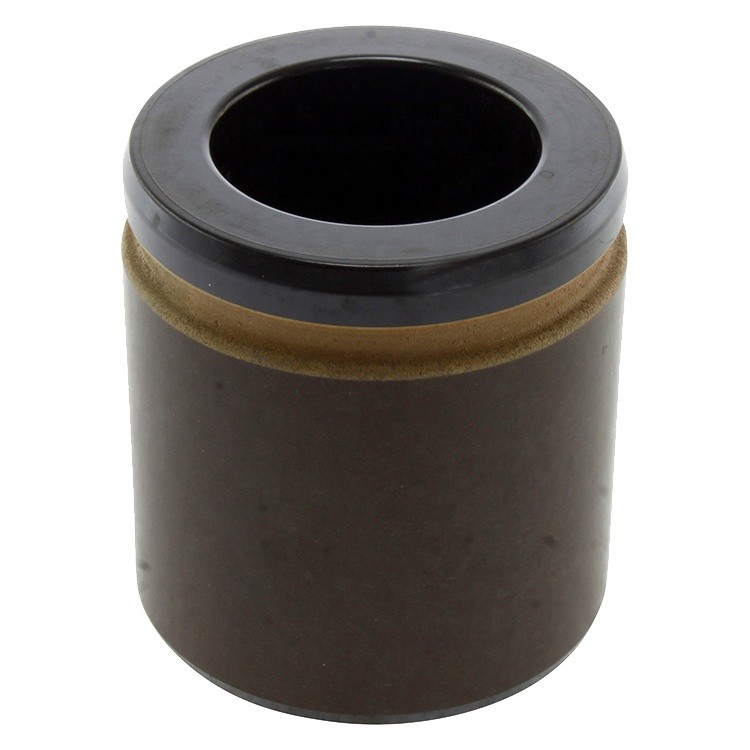
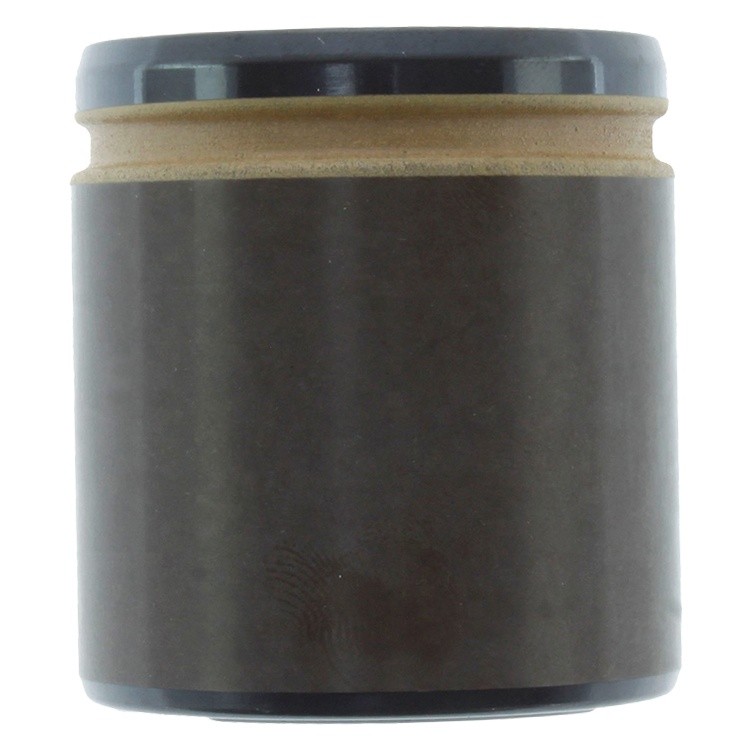
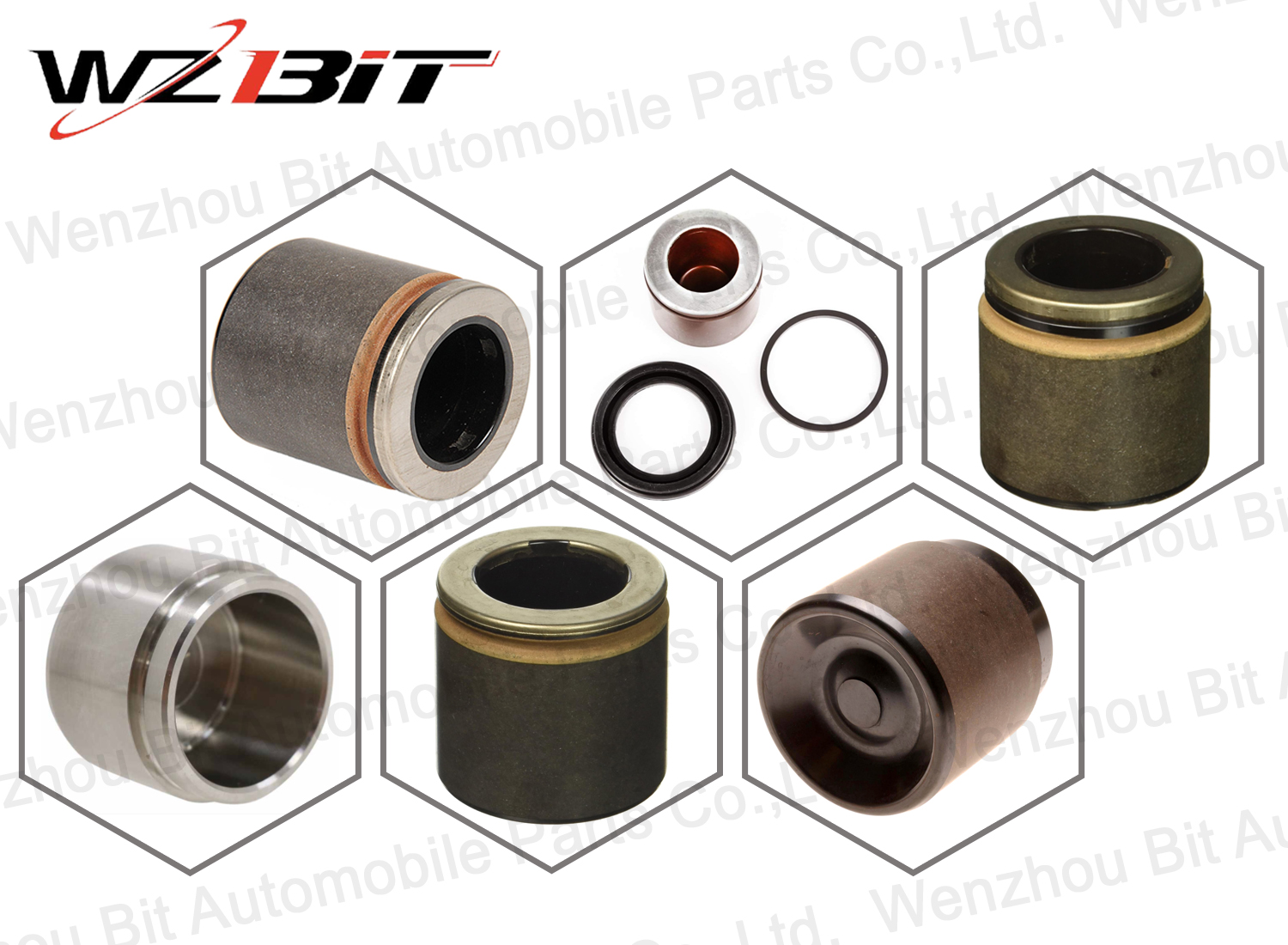
Brake Caliper Piston
 The brake caliper piston is a critical component in a vehicle's disc brake system. It plays a central role in converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force, which presses the brake pads against the brake rotors to slow down or stop the vehicle.
The brake caliper piston is a critical component in a vehicle's disc brake system. It plays a central role in converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force, which presses the brake pads against the brake rotors to slow down or stop the vehicle.

OE Number
14548005
145.48005
Compatible Applications
| CHEVROLET COLORADO 2009-2012 |
| CHEVROLET SSR 2006 |
| CHEVROLET TRAILBLAZER 2006-2009 |
| CHEVROLET TRAVERSE 2009-2017 |
| GMC ACADIA 2007-2017 |
| GMC ACADIA LIMITED 2017 |
| GMC CANYON 2009-2012 |
| GMC ENVOY 2006-2009 |
| ISUZU ASCENDER 2007-2008 |
| JEEP CHEROKEE 2014-2020 |
| JEEP COMMANDER 2006-2010 |
| JEEP GRAND CHEROKEE 2005-2010 |
| SAAB 9-7X 2006-2009 |
| SATURN OUTLOOK 2007-2010 |
Components and Functionality
1. Piston:
- Function: Transmits hydraulic pressure to the brake pads.
- Description: A cylindrical metal component (usually made of steel, aluminum, or phenolic resin) located inside the brake caliper. When hydraulic fluid is forced into the caliper, the piston moves outward, pushing the brake pads against the rotor.
2. Caliper Housing:
- Function: Encases the piston and other components.
- Description: The main body of the caliper, usually made of cast iron or aluminum, that houses the piston and provides a structure for the entire braking mechanism.
3. Brake Pads:
- Function: Create friction with the rotor to slow down or stop the vehicle.
- Description: Components with friction material that are pressed against the rotor by the piston to create the necessary stopping force.
4. Dust Boot:
- Function: Protects the piston from dirt and moisture.
- Description: A rubber boot that covers the outer end of the piston, preventing contaminants from entering the caliper and ensuring smooth piston movement.
5. Seal:
- Function: Prevents brake fluid leakage and ensures pressure is maintained.
- Description: A rubber seal located inside the caliper housing around the piston. It keeps the hydraulic fluid from leaking and maintains the hydraulic pressure needed for braking.
Types of Caliper Pistons
1. Single Piston Caliper:
- Usage: Common in many vehicles, particularly front brakes.
- Functionality: Uses one piston to press the brake pad against the rotor. Simpler design, easier to service.
2. Dual Piston Caliper:
- Usage: Often found in higher-performance vehicles and trucks.
- Functionality: Uses two pistons, providing more even pressure distribution and better braking performance.
3. Multiple Piston Caliper (4, 6, or more pistons):
- Usage: High-performance and racing vehicles.
- Functionality: Uses multiple pistons for superior braking power and more uniform pad wear.
Operation
1. Brake Pedal Application:
- When the brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid from the master cylinder is forced into the brake caliper.
2. Hydraulic Pressure:
- The increased hydraulic pressure pushes the piston(s) outward.
3. Brake Pad Engagement:
- The piston(s) push the brake pads against the brake rotor, creating friction that slows down or stops the vehicle.
4. Release:
- When the brake pedal is released, the hydraulic pressure decreases, and the piston retracts slightly due to the seal's elasticity, allowing the brake pads to move away from the rotor.
Maintenance and Issues
1. Inspection:
- Regularly inspect the brake caliper piston and surrounding components for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Check the dust boot and seals for any signs of tearing or leakage.
2. Lubrication:
- Ensure that the piston and seals are properly lubricated with brake fluid to maintain smooth operation. Do not use other lubricants as they can damage the rubber components.
3. Brake Fluid:
- Regularly check and maintain the brake fluid level. Contaminated or old brake fluid can cause corrosion and damage to the piston and other brake components.
4. Common Issues:
- Sticking Piston: A piston that does not retract properly can cause continuous brake pad contact with the rotor, leading to excessive wear and overheating.
- Leaks: Brake fluid leaks around the piston can indicate seal failure, which can lead to loss of braking power.
- Corrosion: Corrosion on the piston surface can impair its movement and cause uneven braking.
Proper maintenance of the brake caliper piston is crucial for the overall performance and safety of the braking system. Regular inspections and timely replacement of worn components ensure that the brakes function efficiently and reliably.
Send your message to us: