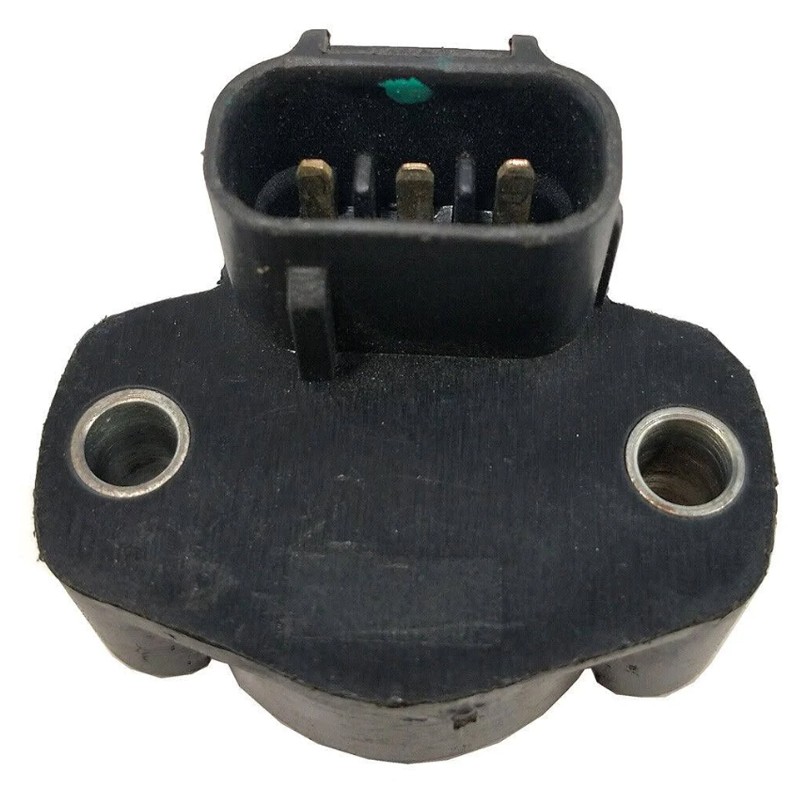
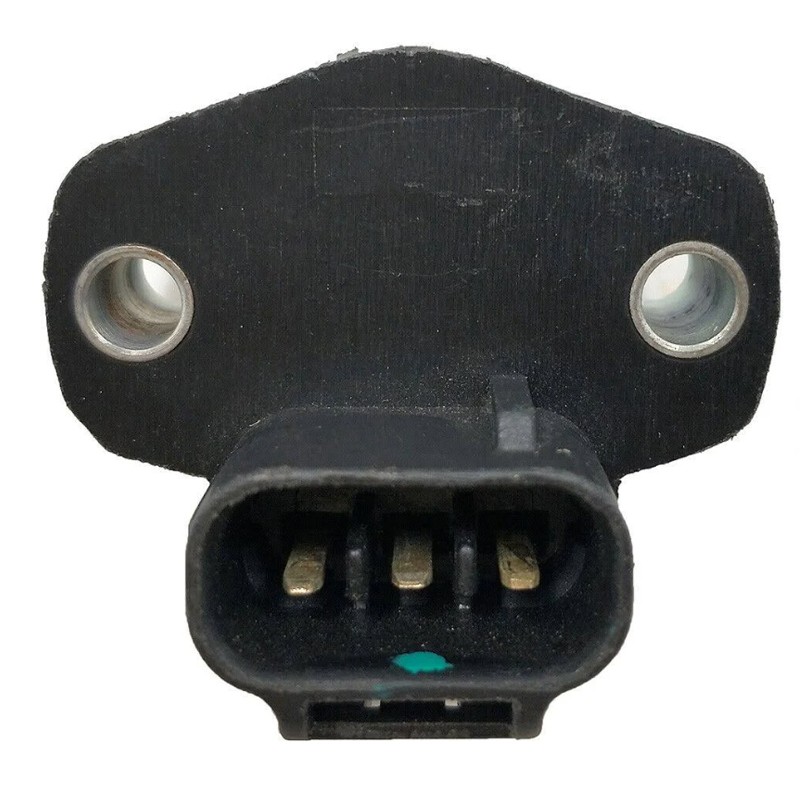
Throttle Position Sensor
A throttle position sensor (TPS) is a crucial component in modern automotive engines that monitors the position of the throttle valve.

OE Number
Compatible Applications
4874371
4874371AB
4874371AC
56027942
DODGE Dakota II (Year of Construction 10.1995 - 09.2003, 120 PS, Petrol)
DODGE Viper RT/10 Convertible (Year of Construction 10.1991 - 09.2002, 407 - 455 PS, Petrol)
DODGE Viper RT/10 SR Coupe (Year of Construction 10.1997 - 09.2002, 455 PS, Petrol)
JEEP Cherokee II (XJ) (Year of Construction 10.1984 - 09.2001, 118 - 185 PS, Petrol)
JEEP Grand Cherokee I (ZJ, ZG) (Year of Construction 09.1991 - 04.1999, 177 - 241 PS, Petrol)
JEEP Grand Cherokee II (WJ, WG) (Year of Construction 04.1999 - 09.2005, 190 - 223 PS, Petrol)
JEEP Wrangler II Off-Road Cabrio (TJ) (Year of Construction 08.1996 - 04.2007, 118 - 177 PS, Petrol)
Function
The primary function of a throttle position sensor is to monitor the position of the throttle valve, which controls the amount of air entering the engine. The sensor detects the angle of the throttle plate and sends this information to the engine control unit (ECU). Based on the throttle position data, the ECU adjusts the air-fuel mixture for optimal engine performance and efficiency.
Construction
Throttle position sensors can use different technologies to detect throttle position, including:
- Potentiometer: Most TPS sensors use a potentiometer, which is a variable resistor that changes resistance with throttle position. The ECU interprets the voltage signal from the TPS to determine throttle position.
- Hall Effect Sensor: Some newer TPS sensors use a Hall effect sensor, which detects changes in magnetic fields generated by the throttle position.
Importance
- Engine Performance: The TPS plays a crucial role in engine performance by providing real-time feedback to the ECU, allowing it to adjust the fuel injection timing and air intake levels for optimal combustion.
- Driveability: Proper functioning of the TPS ensures smooth acceleration, idle control, and throttle response.
- Emissions Control: By accurately monitoring throttle position, the TPS helps optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, contributing to environmental compliance.
Maintenance
Like all sensors, TPS sensors can wear out over time due to exposure to engine heat, vibration, and contaminants. Symptoms of a failing TPS include:
- Check Engine Light: Illuminated due to TPS malfunction or out-of-range readings.
- Erratic Engine Behavior: Such as surging, hesitation, or stalling, especially during acceleration or deceleration.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Incorrect throttle position readings can lead to inefficient fuel combustion.
Replacement
If diagnostic tests indicate TPS failure or if symptoms suggest TPS malfunction, the sensor should be replaced. Replacement involves locating the TPS, disconnecting electrical connectors, removing the old sensor, and installing a new sensor according to manufacturer specifications. Proper calibration may be necessary to ensure accurate throttle position readings.
Summary
The throttle position sensor is a critical component that monitors throttle valve position to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of TPS sensors are essential for ensuring reliable engine operation and vehicle drivability.
Send your message to us: