Coolant Water Temperature Sensor
The coolant temperature sensor (CTS) is a crucial component in a vehicle's engine cooling system. It monitors the temperature of the engine coolant and provides this information to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
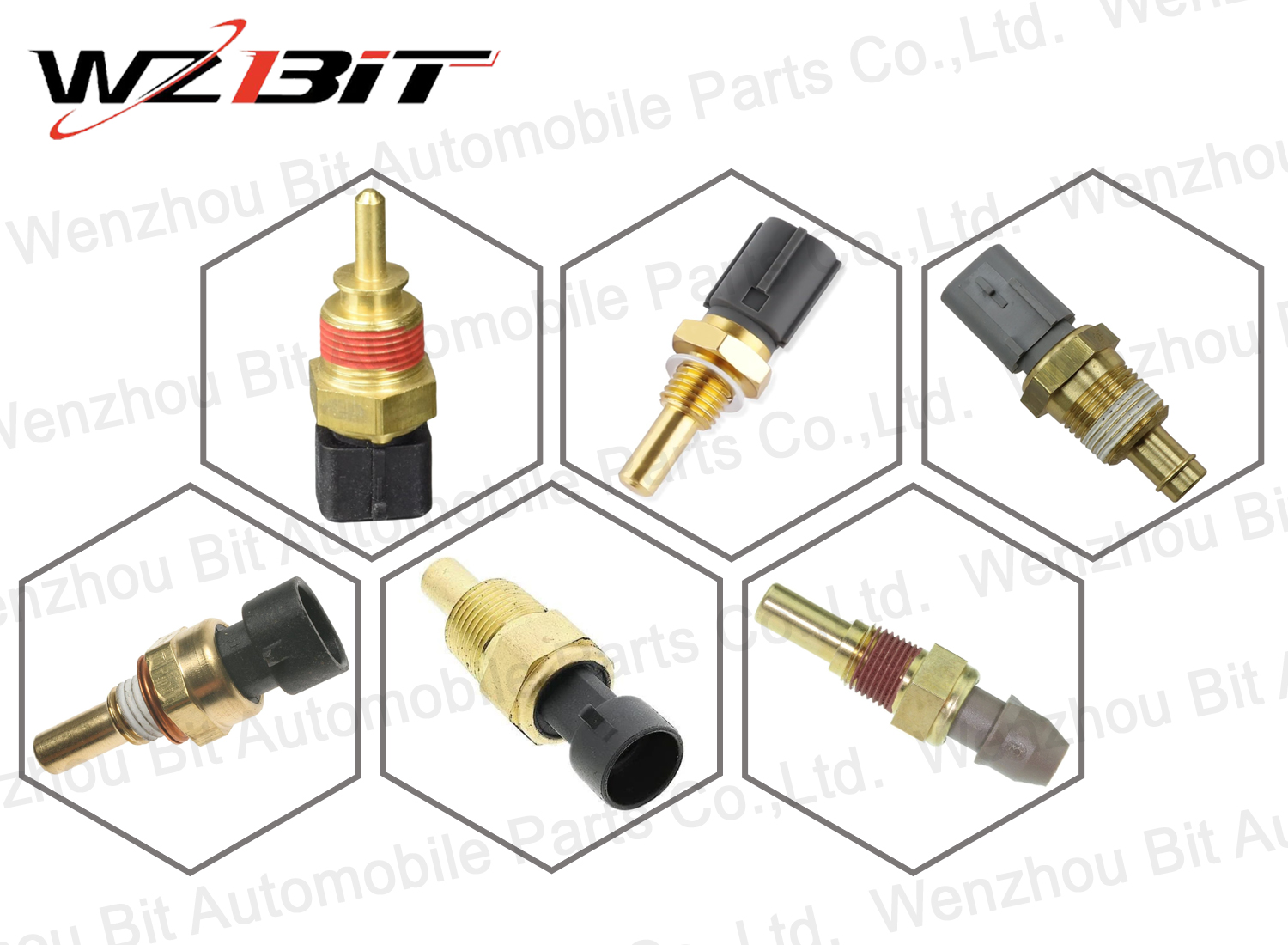

9810048680 / 98 100 486 80
Compatible Applications
CITROËN BERLINGO 2008-2010
CITROËN C3 II 2009-2013
CITROËN C3 PICASSO 2009-2012
CITROËN C4 Coupé 2008-2011
CITROËN C4 GRAND PICASSO I / II 2008-2014
CITROËN C4 I / II 2008-2016
CITROËN C4 PICASSO I / II 2008-2014
CITROËN C5 III 2009-2010
CITROËN DS3 2009-2015
CITROËN DS4 2011-2015
CITROËN DS5 2011-2015
DS 5 2015-2018
DS 4 / DS 4 CROSSBACK 2015-2018
DS 3 2015-2019
PEUGEOT RCZ 2010-2015
PEUGEOT PARTNER TEPEE 2009-2016
PEUGEOT PARTNER - à partir de 2010
PEUGEOT508 SW I 2010-2018
PEUGEOT 508 I 2010-2018
PEUGEOT 5008 II - à partir de 2016
PEUGEOT 5008 2009-2017
PEUGEOT 308 SW II / I 2007-2021
PEUGEOT 308 II / I 2007-2021
PEUGEOT 308 CC 2009-2014
PEUGEOT 3008 2009-2016
PEUGEOT 208 I 2012-2019
PEUGEOT 207/207+ 2006-2013
PEUGEOT 207 SW 2007-2013
PEUGEOT 207 CC 2007-2013
PEUGEOT 2008 I - à partir de 2013
Function
- Temperature Monitoring: The primary function of the coolant temperature sensor is to monitor the temperature of the engine coolant.
- Engine Control: The sensor provides real-time data to the ECU, which uses this information to adjust fuel injection timing, ignition timing, and other engine parameters based on the engine’s operating temperature.
- Coolant System Regulation: It helps regulate the operation of the engine cooling fans, ensuring proper cooling under varying engine loads and conditions.
Components
- Temperature-Sensitive Resistor: Most coolant temperature sensors use a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor—a resistor whose electrical resistance decreases as temperature increases.
- Connector and Wiring: Connects the sensor to the vehicle’s electrical system, transmitting the temperature signal to the ECU.
- Housing: Protects the sensor from coolant and engine heat while ensuring accurate temperature readings.
Operation
- Signal Generation: As coolant temperature changes, the electrical resistance of the thermistor inside the sensor changes.
- Signal Interpretation: The ECU interprets the varying resistance as coolant temperature and adjusts engine parameters accordingly.
- Feedback Loop: Based on coolant temperature sensor readings, the ECU can control fuel mixture, idle speed, emissions controls, and other functions to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
Importance
- Engine Performance: Proper functioning of the coolant temperature sensor ensures that the engine operates within the optimal temperature range for efficient combustion and reduced emissions.
- Emissions Control: It helps maintain proper fuel-air mixture and combustion timing, which are critical for minimizing emissions and complying with environmental regulations.
- Diagnostic Tool: The coolant temperature sensor is vital for diagnosing engine issues, as abnormal temperature readings can indicate cooling system problems or sensor failure.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Testing: If there are symptoms of coolant temperature sensor failure (e.g., check engine light, engine overheating), the sensor can be tested using diagnostic tools to verify its operation and signal output.
- Replacement: If the coolant temperature sensor fails due to wear, electrical faults, or contamination, it may need to be replaced. Replacement involves draining coolant (if necessary), disconnecting electrical connectors, and removing the sensor from its mounting location.
In Summary
The coolant temperature sensor plays a critical role in engine performance and emissions control by providing accurate temperature data to the ECU. Regular maintenance and prompt replacement of faulty sensors are essential for maintaining vehicle reliability and performance.
Send your message to us: