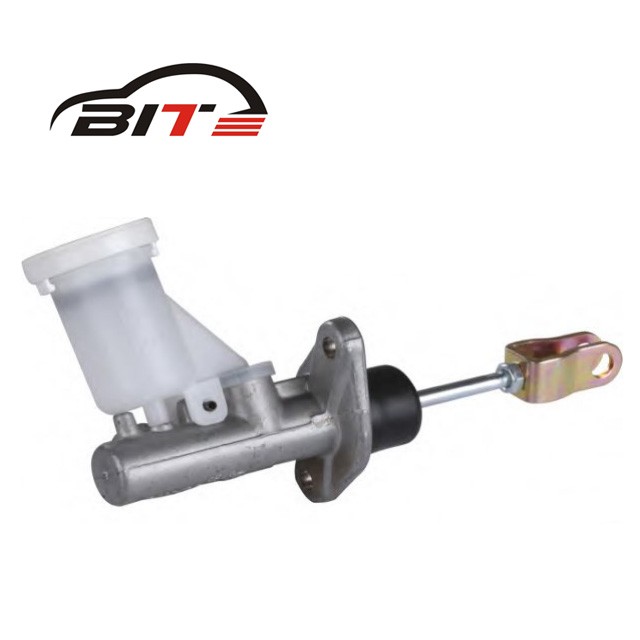
Clutch Master Cylinder
The clutch master cylinder is an essential component of a hydraulic clutch system in vehicles with manual transmissions. Its primary function is to convert the mechanical force from the clutch pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is then transmitted to the clutch slave cylinder to engage and disengage the clutch.

OE Number
MR244839
MB 555274
Compatible Applications
Construction
A typical clutch master cylinder consists of:
- Cylinder Body: Usually made of aluminum or cast iron, housing the internal components.
- Piston: Moves within the cylinder body to create hydraulic pressure.
- Reservoir: A container for the hydraulic fluid, typically mounted on or near the cylinder.
- Seals and O-Rings: Prevent fluid leaks and maintain pressure.
- Push Rod: Connects the clutch pedal to the piston.
- Bleeder Valve: Allows for the removal of air from the hydraulic system.
Operation
1. Pedal Depression: When the driver presses the clutch pedal, the push rod moves the piston within the master cylinder.
2. Hydraulic Pressure: The movement of the piston creates hydraulic pressure in the cylinder, forcing the fluid through the hydraulic lines to the clutch slave cylinder.
3. Clutch Engagement: The hydraulic pressure in the slave cylinder moves its piston, disengaging the clutch and allowing the driver to shift gears.
4. Pedal Release: When the clutch pedal is released, the pressure in the system is relieved, and the clutch re-engages.
Importance
- Smooth Operation: Provides smooth and consistent clutch engagement and disengagement.
- Driver Control: Enables precise control over the clutch, facilitating efficient gear changes.
- Reduced Wear: Hydraulic systems reduce wear on mechanical components compared to cable-operated systems.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance and inspection of the clutch master cylinder are crucial to ensure proper clutch operation:
- Fluid Level: Check the hydraulic fluid level in the reservoir regularly and top up if necessary.
- Fluid Quality: Inspect the fluid for contamination or degradation and replace it as recommended.
- Leaks: Check for fluid leaks around the master cylinder, push rod, and hydraulic lines.
- Pedal Feel: Monitor the clutch pedal for changes in resistance or sponginess, which may indicate air in the hydraulic system or a failing cylinder.
Replacement
If the clutch master cylinder fails or shows signs of wear, it should be replaced to maintain proper clutch function. Replacement typically involves:
1. Accessing the Cylinder: Locate the clutch master cylinder, usually mounted on the firewall in the engine bay.
2. Removing the Fluid: Drain the hydraulic fluid from the reservoir and disconnect the hydraulic lines.
3. Detaching the Cylinder: Remove the bolts or fasteners securing the cylinder to the firewall and disconnect the push rod from the clutch pedal.
4. Installing the New Cylinder: Mount the new master cylinder in place, connect the hydraulic lines, and attach the push rod to the clutch pedal.
5. Refilling and Bleeding: Fill the reservoir with fresh hydraulic fluid and bleed the system to remove air bubbles.
6. Testing: Test the clutch operation to ensure smooth and consistent engagement and disengagement.
In summary, the clutch master cylinder is a vital component in hydraulic clutch systems, converting mechanical force into hydraulic pressure for smooth clutch operation. Regular inspection, maintenance, and timely replacement of the clutch master cylinder are essential for optimal vehicle performance and safety.
MITSUBISHI COLT III (C5_A) (1986/10 - 1992/05)
MITSUBISHI COLT IV (CA_A) (1992/03 - 1996/04)
MITSUBISHI LANCER IV Saloon (C6_A) (1988/04 - 1992/09)
MITSUBISHI LANCER V (CB/D_A) (1992/06 - 1996/12)
MITSUBISHI LANCER V Station Wagon (CB_W, CD_W) (1992/09 - 2003/10)
MITSUBISHI LANCER IV (C6_A, C7_A) (1988/04 - 1994/05)
PROTON PERSONA 400 Hatchback (C9_C, C9_S) (1994/01 - /)
PROTON PERSONA 400 (C9_S) (1994/01 - /)
Send your message to us: