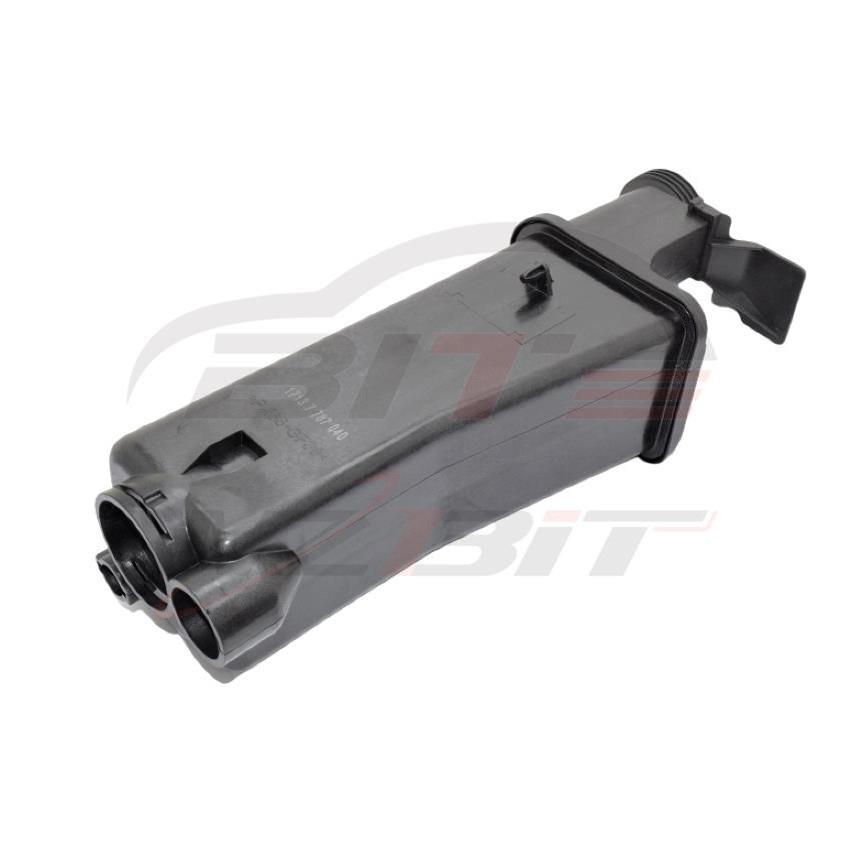
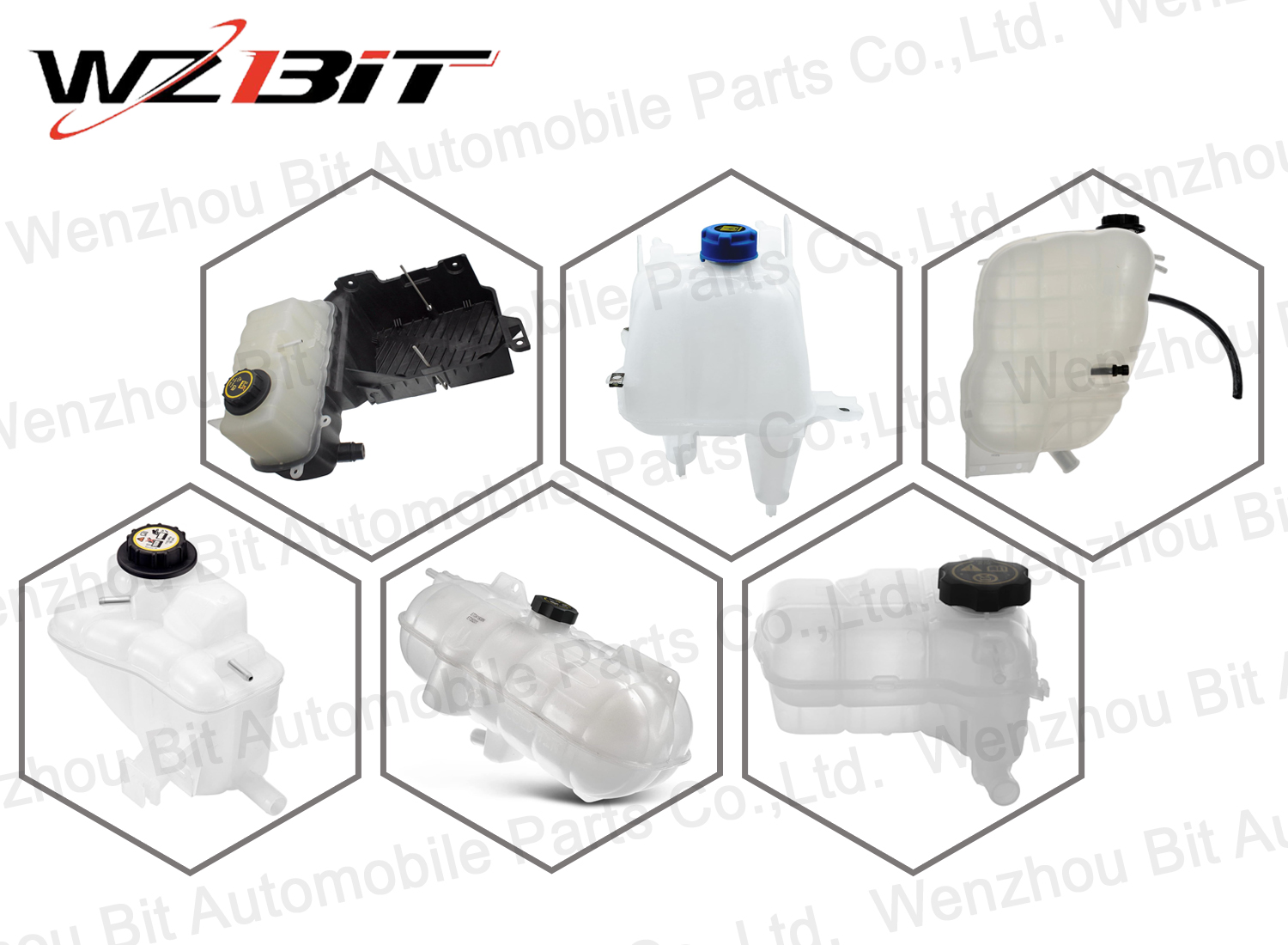
Coolant expansion tank
The coolant expansion tank, also known as the coolant reservoir or overflow tank, serves several key functions within a vehicle's cooling system.

OE Number
| 1436255 | 17137787040 |
| 17111436255 | 2249365 |
| 17112249365 | 7573780 |
| 17117573780 | 7787040 |
Compatible Applications
| BMW 3 Compact (E46) (Year of Construction 09.2001 - 02.2005, 115 - 150 PS, Diesel) |
| BMW 3 Convertible (E46) (Year of Construction 02.2005 - 12.2007, 150 - 204 PS, Diesel) |
| BMW 3 Coupe (E46) (Year of Construction 12.1999 - 07.2006, 105 - 204 PS, Diesel, Petrol) |
| BMW 3 Saloon (E46) (Year of Construction 12.1997 - 05.2005, 105 - 204 PS, Diesel, Petrol) |
| BMW 3 Touring (E46) (Year of Construction 10.1999 - 05.2005, 116 - 204 PS, Diesel, Petrol) |
| BMW X5 (E53) (Year of Construction 04.2001 - 09.2006, 184 - 218 PS, Diesel) |
Function
Its primary role is to provide a reservoir for coolant expansion and contraction as engine temperature fluctuates, thereby maintaining proper coolant levels and system pressure.
Construction
A typical coolant expansion tank consists of:
- Tank Body: Usually made of durable plastic or sometimes metal, designed to withstand coolant and environmental conditions.
- Fill Neck: Includes a cap where coolant can be added to the tank, typically equipped with a pressure relief valve to prevent over-pressurization.
- Level Indicator: Marks or indicators on the side of the tank to show the minimum and maximum coolant levels.
- Hoses and Connections: Attachments for hoses that allow coolant to flow between the tank and the radiator or engine.
- Internal Baffles: Help prevent sloshing and promote consistent coolant level readings.
Operation
1. Coolant Expansion: When the engine heats up, coolant expands. Excess coolant flows into the expansion tank through a pressure relief valve in the radiator cap.
2. Coolant Contraction: As the engine cools, coolant contracts. It is drawn back into the radiator from the expansion tank to maintain optimal coolant levels.
3. Pressure Regulation: Helps regulate system pressure to prevent overheating and ensure efficient coolant circulation.
Importance
- Coolant Management: Provides a buffer for coolant expansion and contraction, preventing overflow or loss of coolant due to temperature changes.
- System Monitoring: Allows visual inspection of coolant levels, ensuring adequate cooling system performance.
- Pressure Relief: Protects the cooling system from excessive pressure buildup, which can cause leaks or component damage.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the coolant expansion tank is essential for optimal cooling system function:
- Inspection: Check the tank regularly for cracks, leaks, or signs of wear.
- Coolant Level: Monitor coolant levels and top up as needed to ensure proper system operation.
- Cap Inspection: Inspect the radiator cap and replace if it shows signs of wear or fails pressure tests.
- Cleaning: Periodically clean the tank and hoses to remove debris or sediment that could affect coolant flow.
Replacement
If the coolant expansion tank is cracked, leaking, or shows signs of damage, it should be replaced promptly to prevent coolant loss and overheating issues. Replacement involves:
1. Cooling System Preparation: Ensure the engine and coolant are cool before starting work.
2. Draining Coolant: Safely drain coolant from the system to prevent spills.
3. Removing Old Tank: Disconnect hoses and remove the old expansion tank from its mounting.
4. Installing New Tank: Install the new expansion tank, reconnect hoses, and secure it in place.
5. Refilling Coolant: Refill the cooling system with fresh coolant, ensuring proper levels and bleeding air from the system.
6. Pressure Test: Conduct a pressure test to ensure the system maintains proper pressure and check for leaks.
In summary, the coolant expansion tank plays a crucial role in maintaining proper coolant levels and pressure within the vehicle's cooling system. Regular inspection and maintenance help ensure efficient engine cooling and prevent potential overheating issues.
Send your message to us: