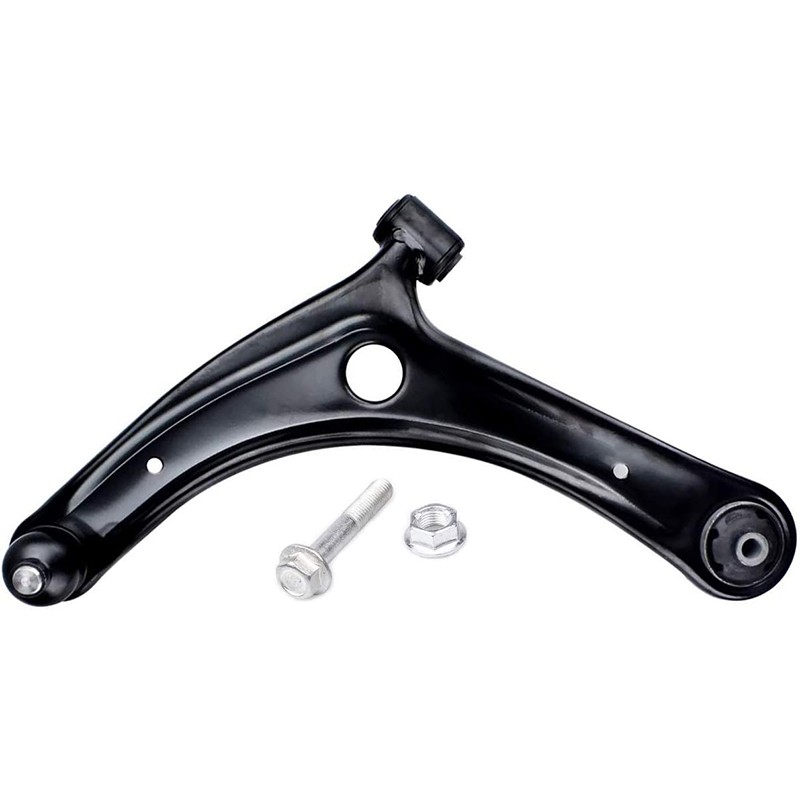
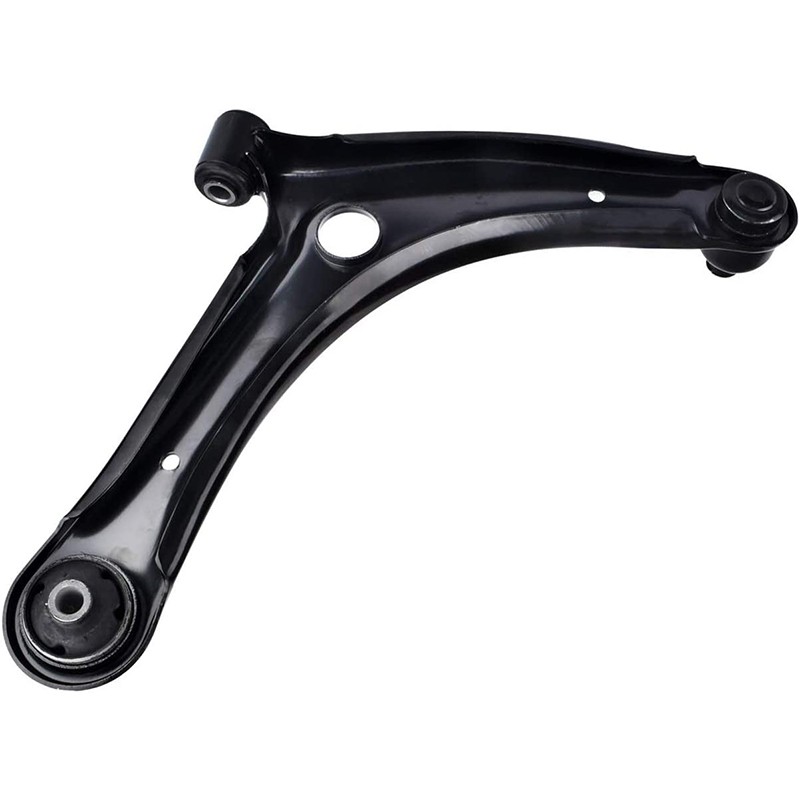
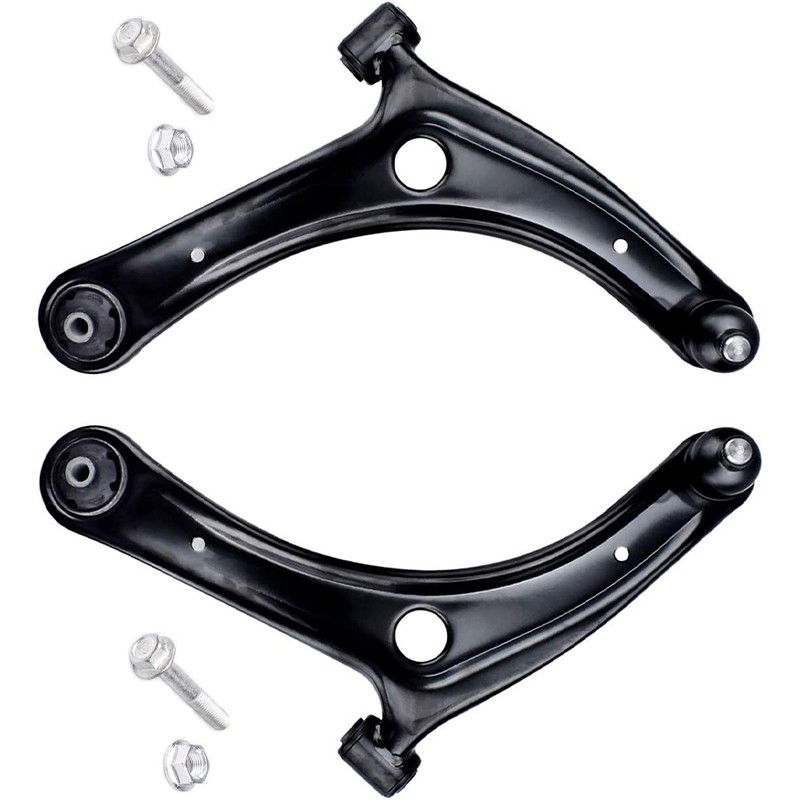
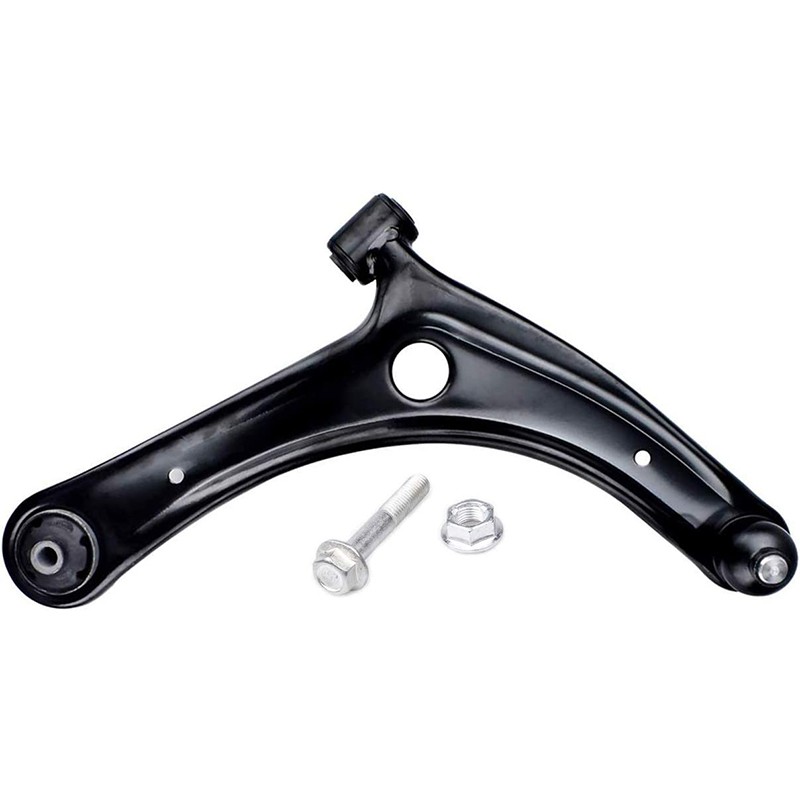
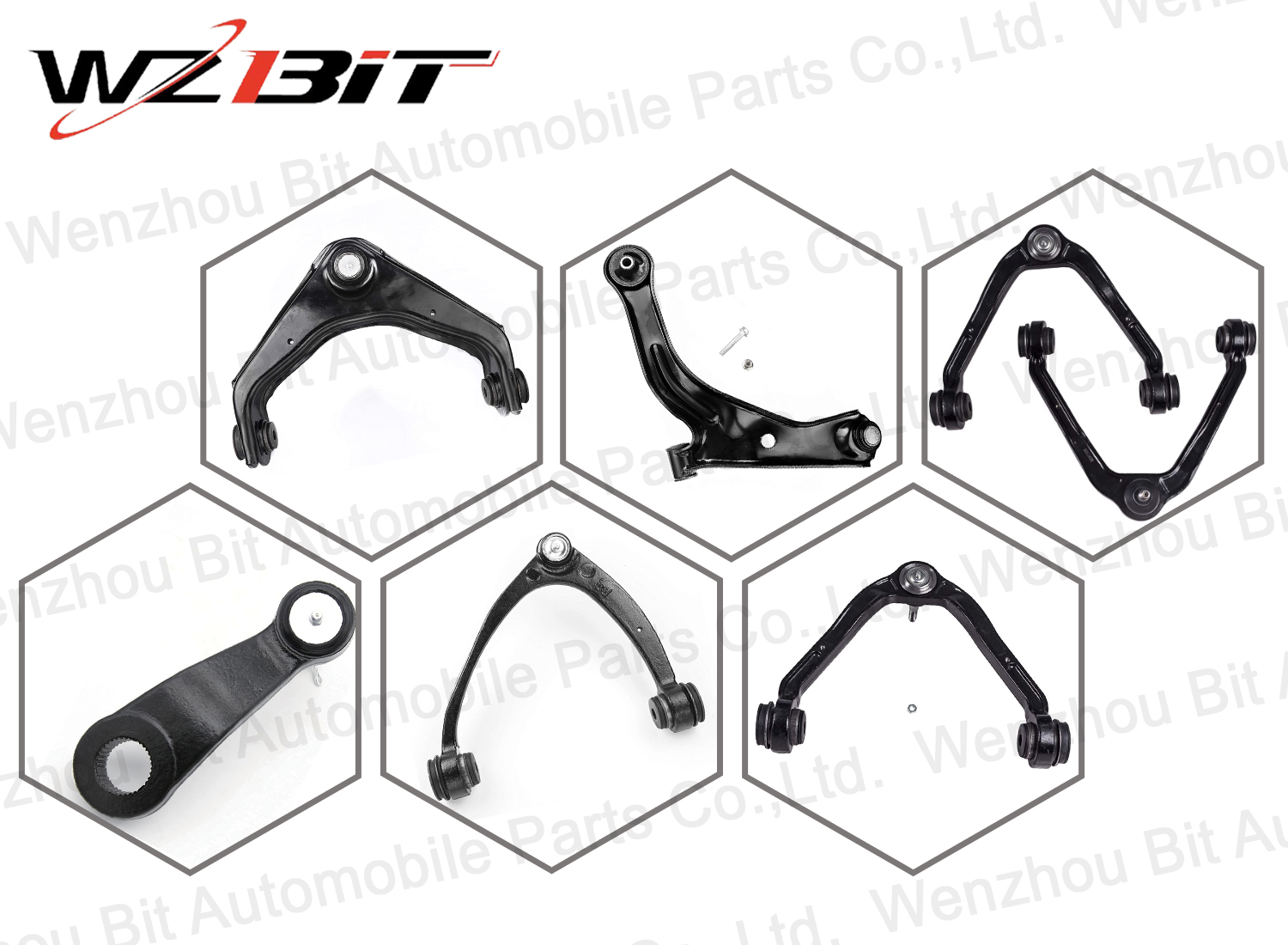
Control Arm
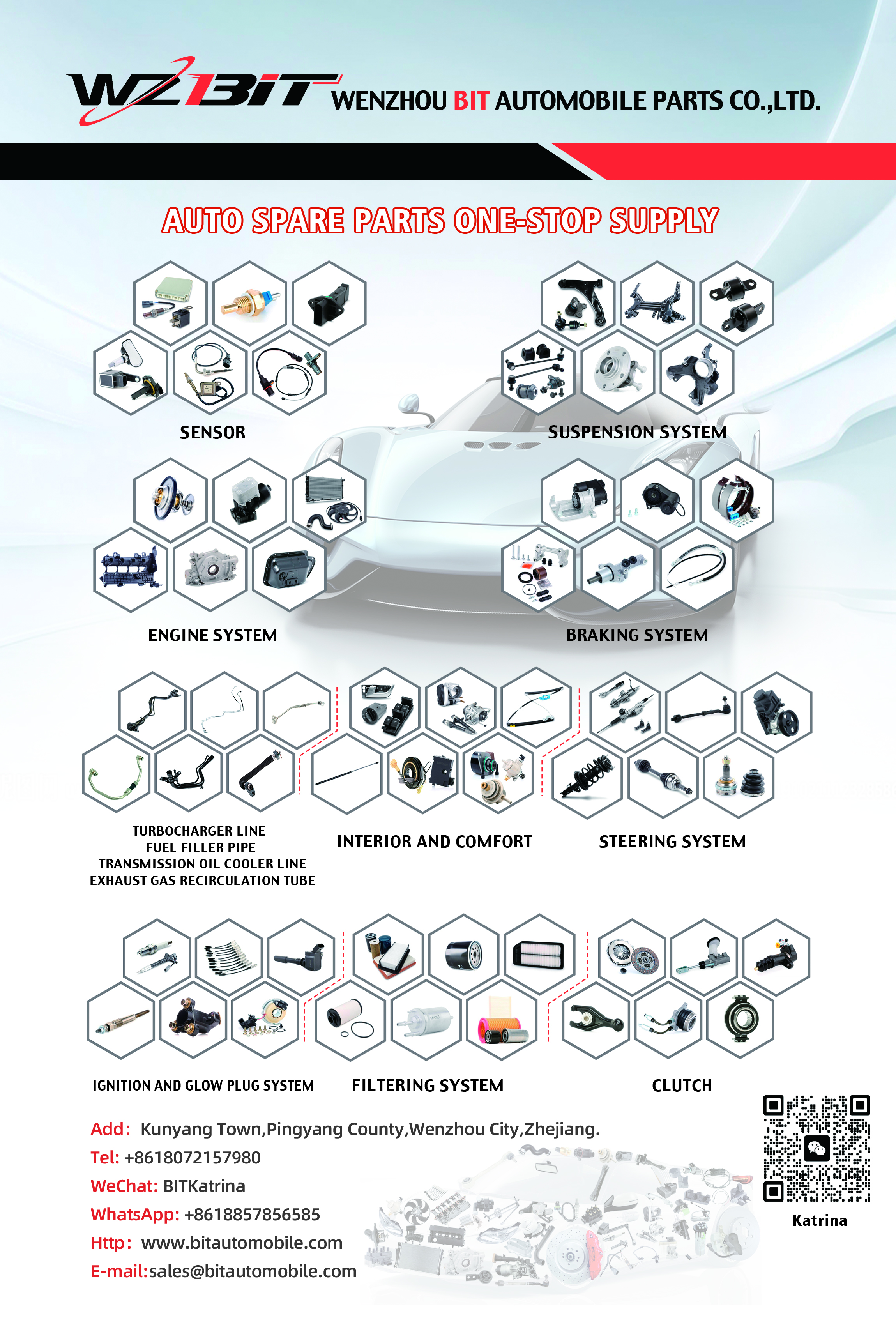 The control arm, also known as an A-arm or wishbone, is a crucial component in a vehicle’s suspension system. Its primary function is to connect the vehicle's chassis to the wheel hub, allowing for controlled movement and maintaining proper alignment of the wheels relative to the body of the vehicle.
The control arm, also known as an A-arm or wishbone, is a crucial component in a vehicle’s suspension system. Its primary function is to connect the vehicle's chassis to the wheel hub, allowing for controlled movement and maintaining proper alignment of the wheels relative to the body of the vehicle.

OE Nember
5105040AI
5105040AD
05105040AG
05105040AB
5105040AH
5105040AC
05105040AF
05105040AA
5105040AG
5105040AB
05105040AE
CH4511100
5105040AF
5105040AA
05105040AD
K620065
5105040AE
05105040AH
05105040AC
RK620065
Compatible Applications
Dodge Caliber 2007-2012
Jeep Compass 2007-2014
Jeep Patriot 2007-2014
Construction:
A typical control arm consists of:- Arm: A metal, often forged steel or aluminum, structure shaped like an "A" or a wishbone. It has two ends: one end connects to the wheel hub or steering knuckle, and the other to the vehicle's frame.
- Bushings: Flexible rubber or polyurethane components at the ends of the control arm that cushion and absorb vibrations while allowing pivoting motion.
- Ball Joint: A spherical bearing at the wheel end of the control arm that allows for multi-directional movement of the wheel and suspension.
Operation:
1. Wheel Alignment: The control arm maintains the position of the wheel in relation to the vehicle's body, ensuring proper alignment for safe and efficient driving.
2. Suspension Movement: As the vehicle drives over uneven surfaces, the control arm allows the suspension to move up and down, providing a smooth ride.
3. Steering Control: The ball joint allows the wheels to pivot and turn, playing a critical role in steering the vehicle.
Importance:
- Stability and Handling: Provides stability and precise handling by maintaining the correct wheel alignment and absorbing shocks and vibrations.
- Safety: Ensures the wheels stay in proper contact with the road, enhancing traction and braking performance.
- Ride Comfort: Contributes to a smoother ride by allowing the suspension to absorb road irregularities.
Maintenance:
Regular inspection and maintenance of the control arm are crucial for vehicle safety and performance:
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion on the control arm, bushings, and ball joints.
- Noise Monitoring: Listen for unusual noises such as clunking or squeaking, which may indicate worn bushings or ball joints.
- Alignment Check: Monitor for uneven tire wear or changes in vehicle handling, which can indicate control arm issues affecting alignment.
Replacement:
If the control arm shows signs of wear, damage, or failure, it should be replaced to maintain proper suspension and steering function. Replacement typically involves:
1. Lifting the Vehicle: Safely raise and support the vehicle to access the control arm.
2. Removing the Wheel: Remove the wheel to expose the control arm and its connections.
3. Disconnecting Components: Disconnect the ball joint from the wheel hub or steering knuckle, and unbolt the control arm from the vehicle frame.
4. Removing the Old Control Arm: Remove the old control arm along with its bushings and ball joint.
5. Installing the New Control Arm: Install the new control arm, ensuring it is properly aligned and secured with new bushings and ball joint.
6. Reconnecting Components: Reattach the ball joint and secure all bolts to the manufacturer’s specifications.
7. Testing: Lower the vehicle, reinstall the wheel, and test drive to ensure proper operation and alignment.
In summary, the control arm is a vital component that connects the chassis to the wheel hub, maintaining wheel alignment, absorbing shocks, and ensuring smooth suspension movement. Regular inspection, maintenance, and timely replacement of the control arm are essential for safe driving, vehicle stability, and ride comfort.
Send your message to us: